We will have such a solution when 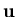 is an eigenvector of
the matrix
is an eigenvector of
the matrix
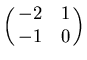 for eigenvalue
for eigenvalue 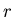 .
The eigenvalues are the roots of the characteristic polynomial
.
The eigenvalues are the roots of the characteristic polynomial
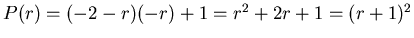 , so the only
eigenvalue is
, so the only
eigenvalue is 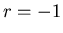 . The equations for an eigenvector are
. The equations for an eigenvector are
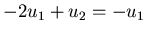 ,
,
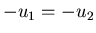 . So the eigenvectors
are the nonzero multiples of
. So the eigenvectors
are the nonzero multiples of
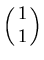 , and the answer
is
, and the answer
is
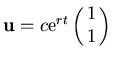 where
where 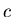 is an arbitrary constant.
is an arbitrary constant.
Robert Israel
2002-04-08
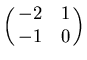 for eigenvalue
for eigenvalue 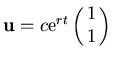 where
where