Summary of Scientific Literature
alpha-1-antichymotrypsin
Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin (ACT) is an acute-phase protein which is over-produced
by reactive astrocytes. It is a protease inhibitor which
suppresses the ability of microglia to remove and rid the
brain of Amyloid-beta fibers.
The secretion of ACT by astrocytes is believed to be
stimulated by the IL-1 cytokine produced by reactive microglia.
A genetic risk-factor for AD is the ACT-A isoform of the
ACT gene. This gene increases susceptibility to the disease.
Quantitative data for the rates of secretion, amounts, and
effects of ACT on A-beta fibrillogenesis is still pending.
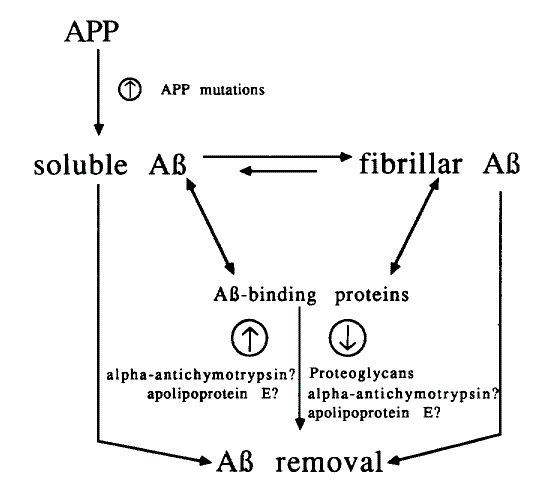
The following
diagram, from Schaffer et al (1995)
summarizes the effects of ACT and ApoE :
See alpha-1-ACT References

